A complete coating inspection consists of three parts: performance testing of the coating itself, quality control of the coating process, and evaluation of coating performance after coating. The following are some key points of coating inspection:
Coating Performance Testing
After the paint is produced according to the formula, the properties of the paint liquid (liquid paint) that need to be tested are as follows: appearance, transparency, color (color difference), viscosity, fineness , specific gravity, non-volatile matter content (solid content), conductivity, pH value, storage stability , and hazardous substances content.
1. Appearance: Visual inspection. Observe whether the coating has any phenomena such as delamination, muddy, thickening, gelation, crusting, precipitation, etc.
2. Transparency: Mainly refers to transparent varnish and base material, tested by visual inspection and standard liquid comparison, using iron-cobalt colorimeter and color assessment cabinet .
3. Color (color difference): Visual inspection. The difference between the liquid color of solvent-based paint and the color of the dry film on the spray panel is not particularly large. The color difference between the dry and wet films of water-based paint is obvious, mainly to see whether there is any floating color.
4. Viscosity: Depending on the specific type of fluid, select different viscosity measurement tools. Generally, using outflow cups like Ford cup, and rotothinner viscometers.
5. Fineness: The fineness mainly affects the stability and gloss of the paint, and is not often used at the painting site . Use grind gauge to measure .
6. Specific gravity: Also called density, usually measured using specific gravity cup or pressure density cup.
7. Solid content: Weigh 1-2g of sample using an analytical balance, place in a dry and clean constant weight crucible, then place horizontally in a pre-adjusted temperature (80-200°C) oven to dry for 1 hour. Take out and place in a desiccator, cool to room temperature and weigh.
Calculation method:
X (Solid content) = (A-B) / C * 100%
A——Total weight of container and sample after drying;
B——Weight of the container;
C——Weight of the sample taken;
8. Conductivity and pH value: Measured with special instruments.
9. Storage stability: Generally, liquid paint is placed in a sealed container and stored in a constant temperature box at 50°C. After a certain period of time, the paint is taken out and retested for various properties to verify its storage stability. Of course, the paint can also be stored in a natural environment for a certain period of time to observe the sedimentation, mold, crusting, particle size (coarsening), etc.
10. Hazardous substance content (VOCs content, heavy metals, etc.): Generally, it is based on the test report of a third-party authoritative organization. Due to the professionalism of its test methods and testing instruments, the market and users currently recognize third-party test data.
Quality Control of Coating (Film)
When the coating has passed the inspection , it is time for the coating inspection , which includes the inspection of physical properties, chemical properties, and construction properties . For ease of understanding , this article lists the spray panel inspection as coating inspection, but in actual application, the coating manufacturing process to simulate the downstream use environment (Upstream product simulation for downstream use of inspection program logic for all product manufacturing processes) for inspection.
1. Appearance of the coating film: Visual inspection. Check for particles, sand marks, welding slag, spray leakage and others.
2. Color (color difference): Visual inspection. Check the consistency and accuracy of the coating color . A colorimeter can also be used for inspection.
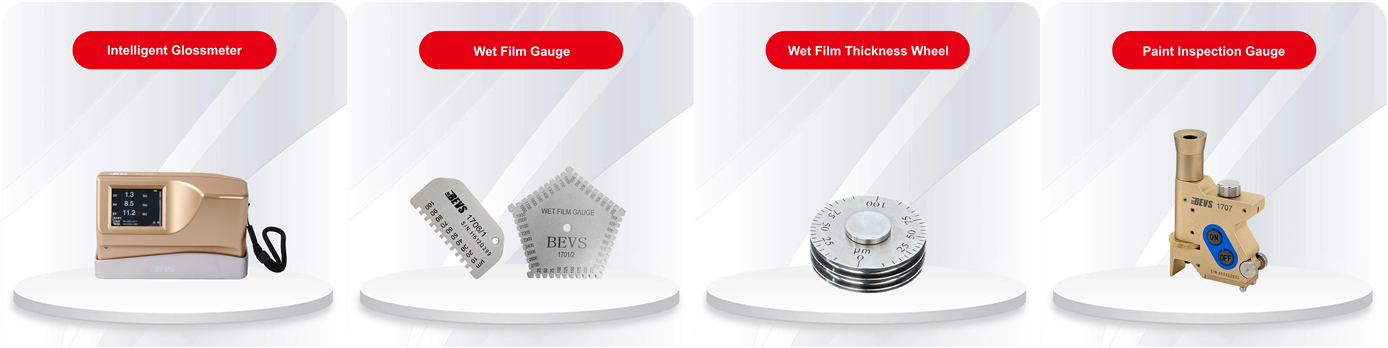
3. Gloss: Measures the ability of the coating film surface to reflect light in a certain direction , using a gloss meter.
4. Film thickness: The thickness of the coating is directly related to its performance quality . The wet film thickness is measured using wet film thickness wheel/wet film gauge , and the dry film thickness is measured using paint inspection gauge.
5. Hardness: To evaluate the mechanical strength and deformation resistance of the coating , pencil hardness test method, pendulum damping hardness test method and indentation hardness test method are used. Special instruments are required, such as pencil hardness tester, pendulum hardness tester and buchholz indentation tester.
6. Adhesion: Coating adhesion is the degree of firmness of the bond between the coating and the substrate, which is crucial to the performance and service life of the coating . When testing a single coating, the cross-cutting method and the circle-cutting method are often used, using hatch gauge / cross hatch cutter, automatic cross hatch instrument , and automatic circle-cutting method tester. When testing thicker coatings (such as putty) and both single coating layer/multi layer coating systems, the pull-off method is more appropriate, automatic pull-off adhesion tester is used.
7. Flexibility: The flexibility of the coating affects the durability and performance of the coating . The shaft rod measuring method , cylindrical shaft bending tester method and cone flexure tester method are used . Cylindrical bend tester and conical bend tester are used.
8. Abrasion resistance: Evaluate the durability of coating in practical application . Commonly used methods include rotating friction rubber wheel method, reciprocating motion wear test method , wear resistance test method , rotating rubber grinding wheel method , using scratch tester, abrasion tester and others.
1. Acid and alkali resistance: Both are measured using 0.1 mol/L HCl and NaOH solutions, generally using Method A, i.e. the immersion method.
2. Resistance to water, oil, and diesel: A method immersion method is generally used for testing.
3. Heat and humidity resistance: Tested with special instruments in temperature and humidity control chamber.
4. Salt spray resistance: According to a large number of experimental surfaces, the paint film has the highest corrosion rate in 5% salt water, so the salt spray salt concentration is 5% salt water, including NSS (neutral salt spray), AASS (acetic acid salt spray) and CASS (copper salt accelerated acetic acid salt spray). Generally, the NSS experimental method is the main one, and other coatings will be mainly CASS. The equipment used is a salt spray tester.
5. Artificial accelerated aging: Using the principle of light absorption to simulate sunlight exposure, the sample is aged faster in a warm, humid, and light environment. Xenon arc lamps are generally used . When focusing on ultraviolet light aging tests , UV lamps can be used. The equipment used is xenon aging tester and UV weather tester.
6. Chemical wiping resistance: Special requirements, mainly seen in 3C products and plastic parts, solvent or alcohol wiping resistance. Multifunction abraser can be used .
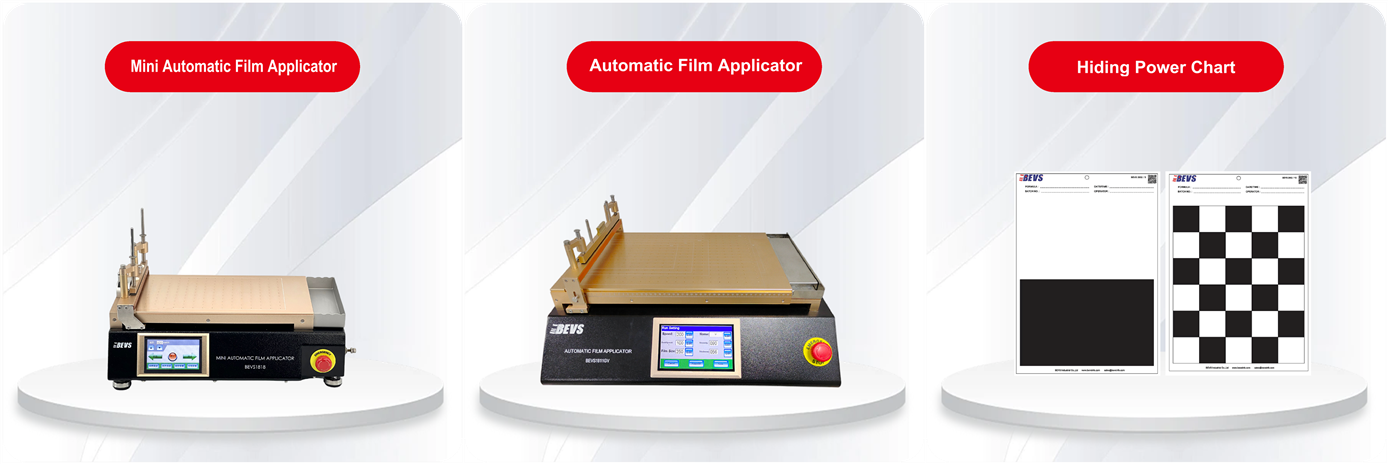
1. Hiding power: refers to the ability of the coating to cover the substrate, which is generally reflected in the coating with more "bright" colors. Its brightness is higher and the coloring pigment is more expensive. The common reflectivity method uses an applicator to apply on black and white card paper or colorless and transparent polyester film, and determines the hiding power by measuring the reflectivity. Usually use Hiding power chart, and various specifications of film applicators.
2. Coating rate, painting rate, loss coefficient: Depending on the structure of the workpiece and the hanging angle, there is a theoretical coating rate. The specific calculation formula is not recommended and it is still subject to the evaluation of actual application.
3. Sagging and leveling: Leveling refers to the ability of the irregular and uneven surface of the coating film to flow into a flat and smooth surface after the coating is applied. It is measured using a leveling meter. Sagging refers to the phenomenon that when a liquid coating is applied on a vertical surface, the surface of the wet film flows downward due to the influence of gravity, causing the upper part of the coating film to become thinner and the lower part to become thicker. In severe cases, it forms a spherical or wavy shape. It is measured using a sagging applicator.
4. Drying time: refers to the time required for the paint to change from liquid to solid . There are different regulations such as surface drying, touch drying, and actual drying. In practical applications, it can be measured by the finger touch method, blade method, etc., or by drying time recorder .
Coating inspection is a systematic work that needs to be carried out strictly in accordance with standards and processes to ensure the performance and quality of the paint. Through the above tests, the applicability and coating effect of the paint can be comprehensively evaluated, providing a scientific basis for the selection and application of the paint.