Pertence à categoria: Seminar
Data de lançamento: 2025-02-06
Taxa de clique: 5490
A editora: Ivy
Coleção:
Adhesion refers to the mutual attraction between two different materials at their contact points. In coatings, adhesion refers to the ability of a coating film to bond to the substrate surface or between layers of the coating through physical and chemical interactions.
Adhesion is a critical technical indicator for evaluating coating quality. Coatings with good adhesion are durable and meet performance requirements, whereas coatings with poor adhesion may blister, crack, or peel, affecting their usability.
Factors Affecting Coating Adhesion
· Substrate Cleanliness: Insufficient cleaning of the substrate can prevent proper adhesion.
· Surface Texture: Smooth surfaces may not hold the coating well.
· Wetting of the Coating: Poor wetting on the substrate affects adhesion.
· Curing Issues: Under-curing, over-curing, or inadequate cross-linking can reduce adhesion.
· Environmental Factors: Moisture, UV radiation, and other environmental factors can degrade adhesion.
These factors may cause surface defects such as:
· Blistering: Dome-shaped defects caused by trapped moisture, rapid drying, or chemical exposure.
· Peeling: Loss of adhesion due to contamination or incompatibility.
· Delamination: Separation of the paint layer from the substrate.
· Undercutting: Corrosion buildup under the coating.
Common Coating Adhesion Testing Methods
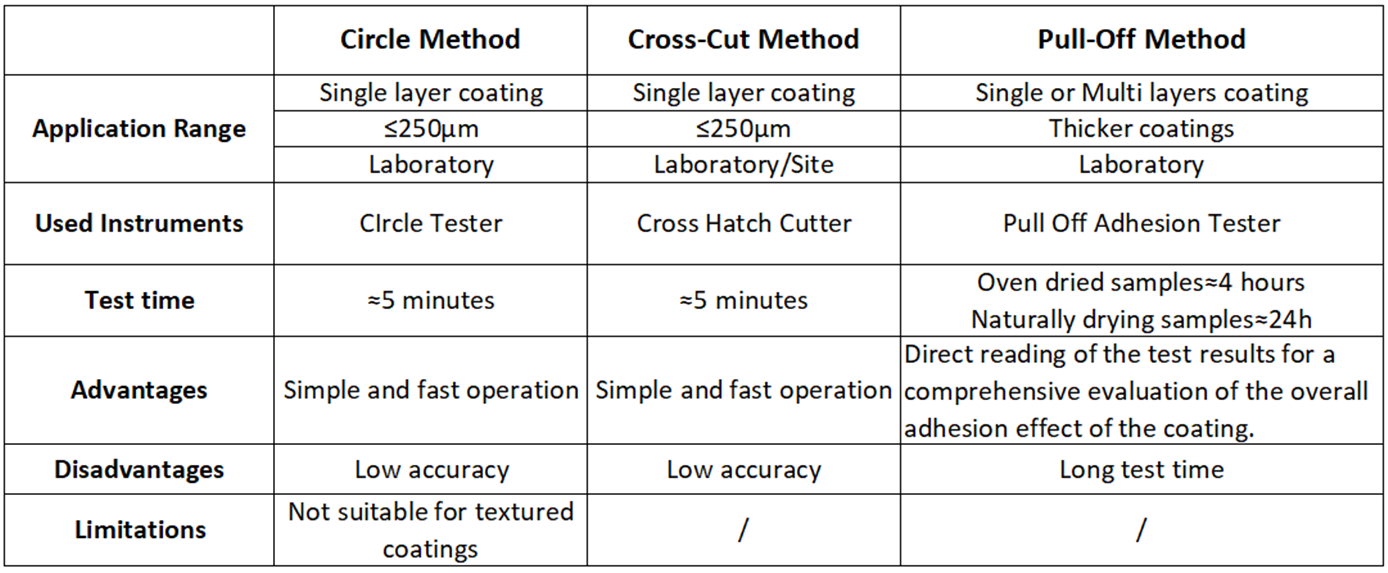
The primary methods for testing coating adhesion are the circle method, cross-cut method, and pull-off method, each with unique features and applicability.
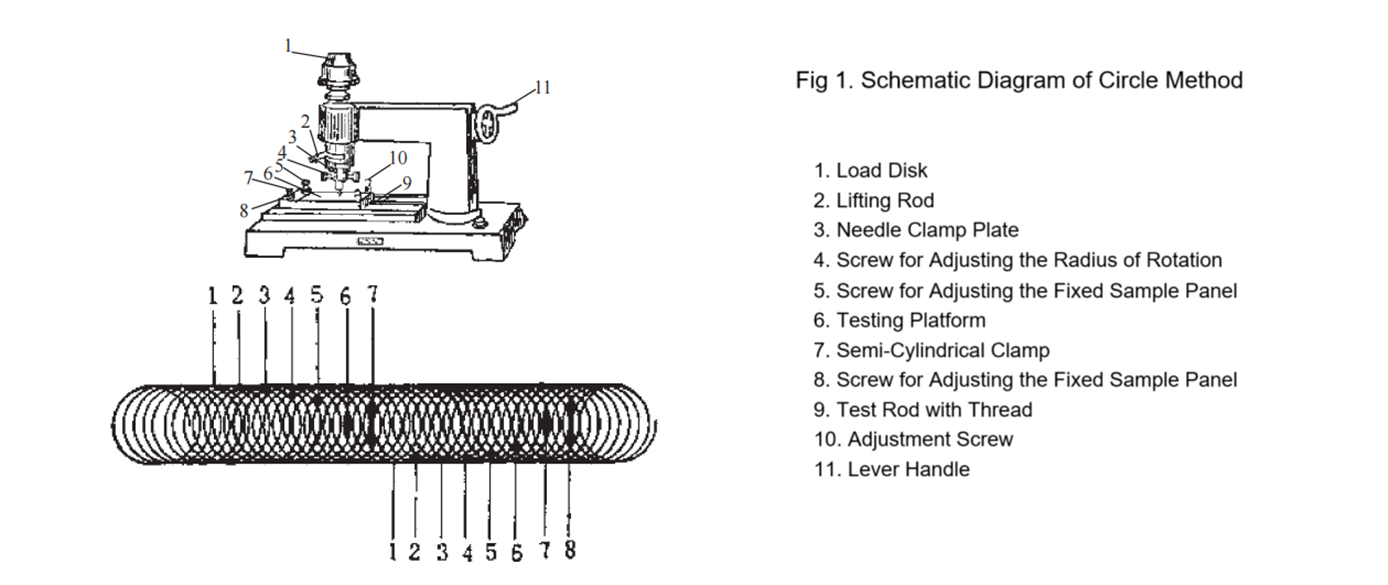
A pointed needle penetrates the substrate under a specified load, tracing a circular motion of a fixed diameter. Adhesion is evaluated based on the damage area caused to the coating.
A cutting tool creates a grid pattern on the coating, penetrating to the substrate. Adhesion is assessed by the resistance of the coating to detachment, with results based on the area of coating removal. The grid spacing depends on the coating thickness and substrate type.
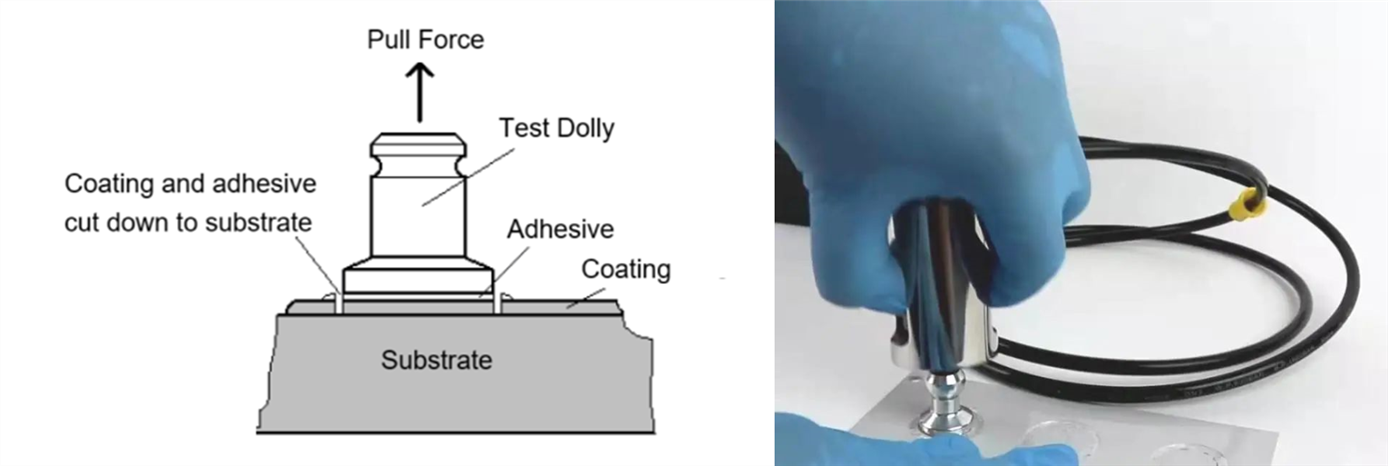
Also called the "tensile method," it measures the force required to detach the coating from the substrate by applying vertical tension at a controlled speed. Results are expressed as tensile force per unit area (MPa). This method evaluates both interlayer adhesion and substrate bonding. It is a comprehensive method for assessing overall adhesion performance but requires adhesives to cure fully before testing, leading to longer test times.
Pull-off adhesion testers are generally divided into two categories: manual and automatic. Manual testers, due to improper operation or uneven application of force, often result in data fluctuations. In contrast, automatic testers offer greater advantages in terms of measurement accuracy and ease of use.
Common Coating Adhesion Testing Methods
Each of the three testing methods has its own advantages and disadvantages, as summarized in the following table:
Circle Method and Grid Method:
Both are classified as indirect testing methods, with results expressed in qualitative grades. These methods rely heavily on visual judgment, and achieving accuracy during the cutting process can be challenging. Variations in operator experience may lead to errors. However, these methods are simple, fast, and widely used. The grid method is particularly suitable for on-site applications during construction.
Pull-Off Method:
This is a direct testing method that provides quantitative data on coating adhesion. It is an excellent tool for evaluating the compatibility of coating systems and comprehensively assessing overall adhesion performance. It can also serve as an experimental standard for product quality control, helping to improve product quality. However, this method is more complex and requires the adhesive to fully cure before testing, which leads to longer test times.
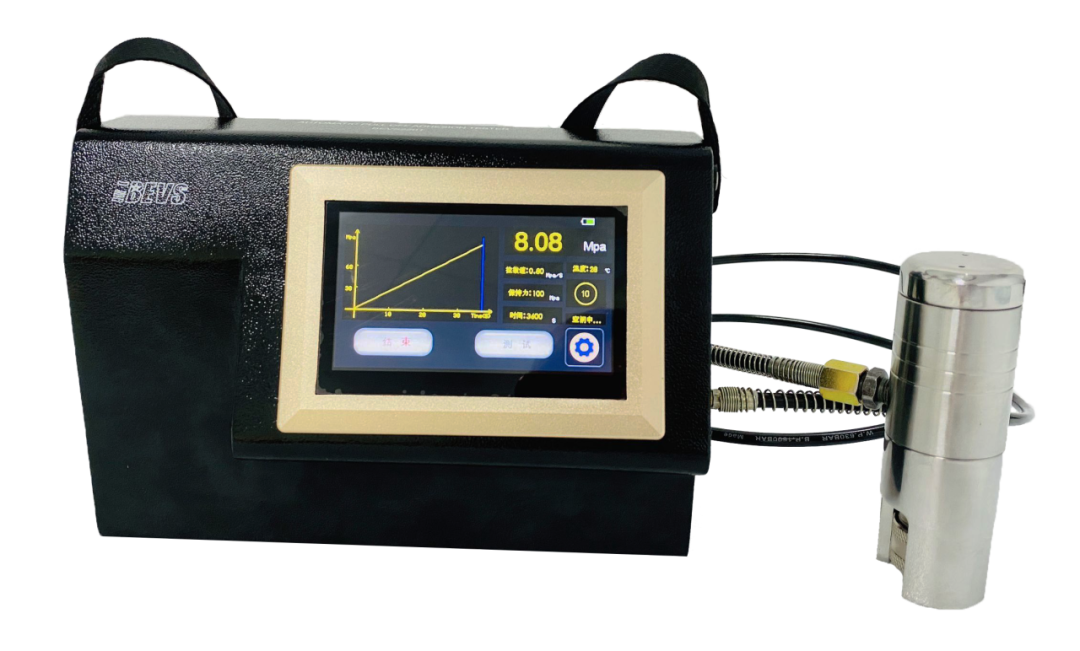
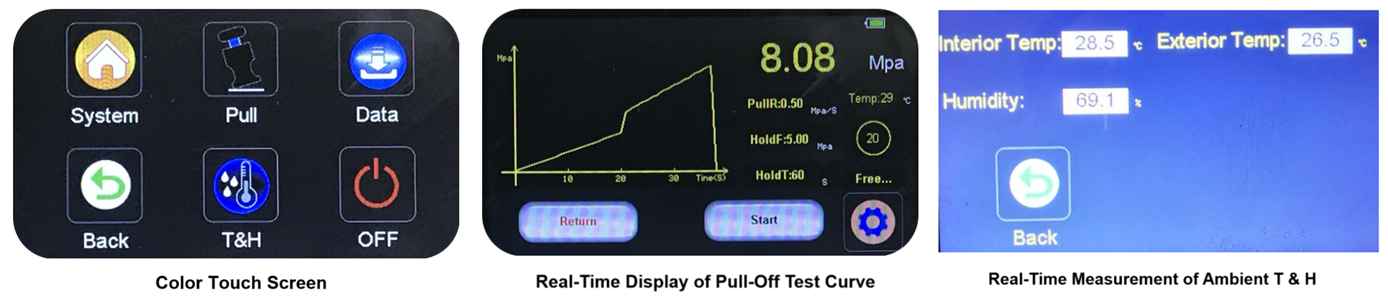
Automatic Pull-Off Adhesion Tester BEVS 2201
This instrument is specifically designed for coating adhesion testing. Each device features a hydraulically calibrated system with an accuracy of ±1%.
Key Features:
· Fully automated operation with precise digital measurements.
· Displays pressure curves, pressure values, pull-off speed, ambient temperature, and device status in real-time.
· Includes 10mm, 14mm, and 20mm dollies, supporting maximum adhesion of 100MPa (14,500 psi) for 10mm dollies.
· Built-in temperature and humidity sensors for environmental monitoring.
· USB data transfer capability and a 20,000mAh rechargeable battery.
Compliance with standards: ASTM D4541/D7234, ISO 4624/16276-1, JIS K 5600 5-7, GB/T 5210-2006. Suitable for quantitative adhesion measurement on metal, concrete, wood, plastic, and other substrates.