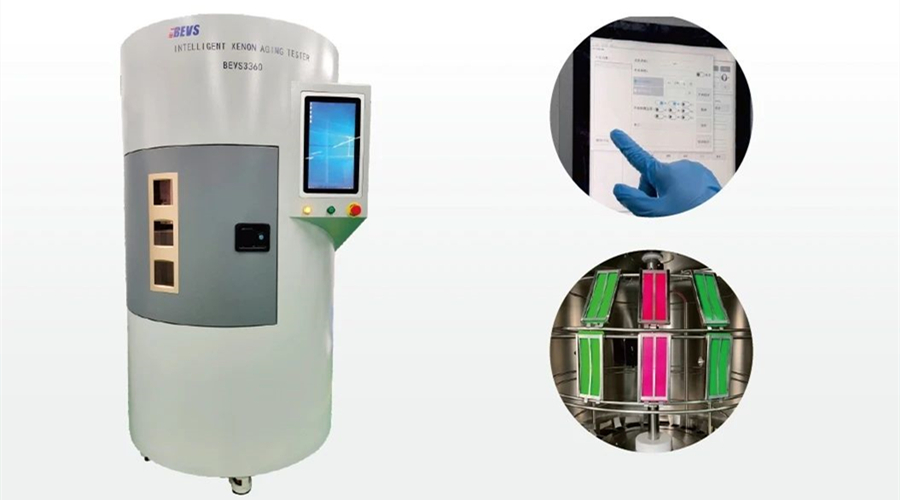
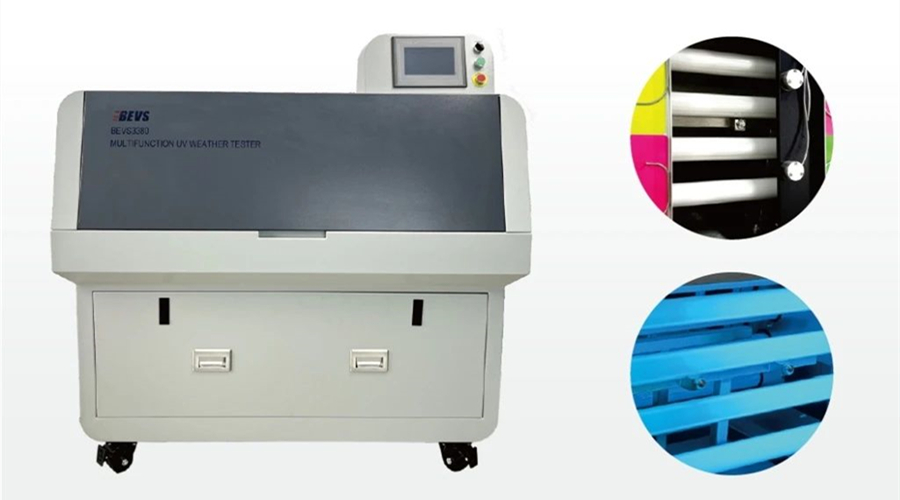
Equipos
- Dispersión
- Densidad / Finura
- Viscosidad
- Aplicación de recubrimiento
- Aplicador de recubrimientos automático compacto
- Aplicadores de recubrimientos automáticos
- Aplicadores de barra
- Aplicador forma “U”
- Aplicador cilíndrico (4 caras)
- Aplicador de cuatro lados con depósito
- Aplicador de forma cúbica
- Aplicador de altura ajustable
- Aplicador de descuelgue
- Aplicador de nivelación
- Varillas de espiral
- Soporte de varillas
- Cartulinas de ensayo
- Aplicador ajustable digital
- Kit de aplicación
- Cabina de aplicacion para paneles con pintura liqu
- Tiempo de secado
- Espesores
- Temperatura
- Color y Brillo
- Adherencia
- Dureza
- Deformation
- Abrasímetro, frote y lavabilidad